Traditional NSAIDs include aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen and many other generic and brand name drugs. A newer NSAID is celecoxib (Celebrex), which doctors call a "COX-2 inhibitor" or a "COX-2 selective" NSAID.
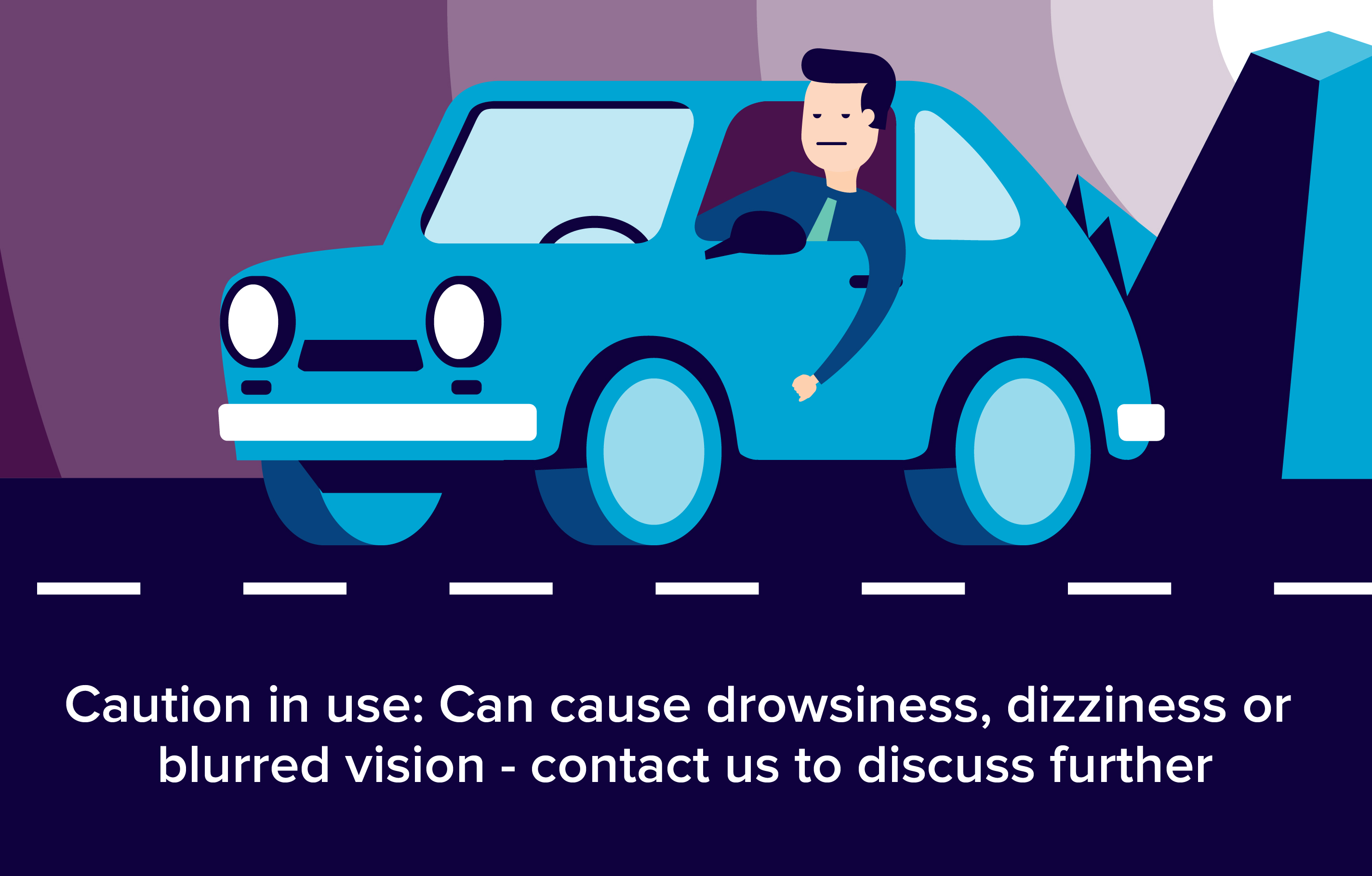
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are some of the most often used pain medicines in adults.
- NSAIDs also can decrease inflammation, such as in arthritis.
- Most people can take NSAIDs without any trouble. Yet side effects are possible, including stomach bleeding, allergic reactions, kidney problems and heart problems.
- Though you can buy many NSAIDs without a doctor's prescription, not everyone should take these drugs. Always talk to your doctor before taking any new medicine.
Uses
NSAIDs are used to relieve pain and reduce signs of inflammation: fever, swelling and redness. People may take NSAIDs for temporary conditions such as sprains, strains, flares of back pain, headache and painful menstrual periods. NSAIDs also are a common treatment for chronic (long-term) health problems such as arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and others) and lupus.
Another use of aspirin is for prevention. A daily low-dose aspirin can help lower the chance of having a heart attack or stroke for people who are at high risk of these serious events.
How they work
NSAIDs work to decrease inflammation, pain and fever. NSAIDs block enzymes in the body that help make prostaglandins, chemicals that play a role in pain and inflammation. Older NSAIDs like ibuprofen block two of these enzymes, COX-1 and COX-2, but celecoxib (Celebrex) targets mainly COX-2. Celecoxib is no more effective than other NSAIDs. However, its possible risks differ from those of other NSAIDs, as the “Side effects” section below explains.
Dosing
Each NSAID has its own dose (strength) and interval for how often to take the drug. The doses of medicines that are over the counter—sold without a doctor's prescription—are often less than prescription doses of the same medicine. For instance, the most common doses of prescription ibuprofen are 400 mg (which stands for milligrams), 600 mg and 800 mg, but the highest dose sold over the counter is 200 mg.
Over-the-counter NSAIDs may be strong enough for temporary conditions such as sprains, strains, flares of back pain, headache and menstrual pain. For chronic health problems such as arthritis or lupus, a rheumatologist will most often prescribe these drugs at higher doses and over a long time.
Time to effect
NSAIDs start to work quickly, most often in less than a few hours. How fast they take effect depends on the intended effect. Pain control tends to occur much quicker than anti-inflammatory (inflammation-fighting) effects, such as for arthritis.
SIDE EFFECTS
All drugs have a risk of side effects, including NSAIDs. It is important to understand the risks and benefits of a drug before deciding to take it. Possible risks of all NSAIDs include, among others:
- Stomach problems like bleeding, ulcer and stomach upset
- High blood pressure
- Fluid retention (causing swelling, such as around the lower legs, feet, ankles and hands)
- Kidney problems
- Heart problems
- Rashes
Many people may assume that over-the-counter medications are safer than the same or similar medicines that need a prescription, but this is not always true. For added safety, the doses of over-the-counter medicines are often less than prescription doses of the same medicine. In equal doses, the safety profile of over-the-counter NSAIDs is the same as for their prescription forms. The risk of side effects does go up with higher doses.
Though side effects can occur at any time you take an NSAID, the chance tends to be greater the longer you take the drug. If you must take NSAIDs for more than 30 days, ask your doctor how to lower your risk of problems. You may need to take extra precautions to avoid side effects, such as taking medicine to lower the risk of stomach bleeding.
There is no clear difference in overall safety among traditional NSAIDs on the market. Side effects of each drug may vary, and some patients may be more prone to the side effects of one drug than another. In some studies, naproxen appears safer on the heart. Celecoxib is somewhat less likely to cause stomach problems, such as ulcers and bleeding, than traditional NSAIDs. Yet some large studies in patients have linked celecoxib to a possible raised risk of heart problems, more so at doses above 200 mg per day.
Warnings: If you have heart disease, you should not take celecoxib or another NSAID, including an over-the-counter NSAID, without first discussing it with your doctor. Some traditional NSAIDs may also interfere with aspirin prescribed to patients with heart disease. As well, mixing aspirin with other NSAIDs raises the risk of stomach bleeding.
NSAIDS should not be used during pregnancy unless your doctor thinks they are necessary.
Some people have other risk factors that raise their chance of having health problems due to NSAIDs. Talk to your doctor before taking an NSAID if any of these risk factors apply to you:
Have any of these health problems
- decreased kidney or liver function, or an uncontrolled liver problem (such as hepatitis)
- ulcer, gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining) or stomach bleeding now or in the past
- low platelet count
- Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
- asthma or chronic lung disease
- reflux disease (also known as GORD), indigestion or hiatal hernia
- high blood pressure, congestive heart failure or a past stroke or heart attack
- Are allergic to aspirin, other NSAIDs, or sulfa drugs, or have nasal polyps (linked to a greater chance of NSAID allergy)
- Take blood thinners or corticosteroids (see “Drug interactions” below)
- Are pregnant, may become pregnant, or are breast-feeding
- Drink more than seven alcoholic drinks per week or more than two in a day
- Age over 65
Doctors have long warned not to give aspirin to children under age 12, but teens with a virus also should avoid drugs containing aspirin. There is a risk of Reye’s syndrome, a rare but deadly illness that can affect the brain and liver.
Drug interactions
Tell your doctor about all of the medications you are taking, even ones that are over the counter or natural remedies. Some medicines increase the risk of side effects of NSAIDs. These include aspirin and other blood thinners like warfarin, heparin and clopidogrel (Plavix) as well as corticosteroids, such as prednisone. If you take any of these medicines, ask your doctor if you can take NSAIDs.
Do not mix an over-the-counter NSAID with a prescribed NSAID, or take more than the recommended dose of the NSAID. Doing so could increase your chance of side effects.
References:
http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Anti-inflammatories-non-steroidal/Pages/Introduction.aspx
http://www.rheumatology.org/Practice/Clinical/Patients/Medications/NSAIDs__Nonsteroidal_Anti-inflammatory_Drugs/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-steroidal_anti-inflammatory_drug
http://arthritis.webmd.com/features/pain-relief-how-nsaids-work
http://www.medicinenet.com/nonsteroidal_antiinflammatory_drugs/article.htm